For my Master's thesis I had the opportunity to join the Center for Engineering Education and Outreach (CEEO) at Tufts University in Boston. As part of their existing research, they developed Smart Motors, an affordable, self-contained, modular robotics box, with a built-in motor, an accelerometer as default sensor, as well as a modular port for an optional external sensor. In its normal use-case, the device has a built-in reinforcement-learning algorithm, which allows the user to map sensor input and motor output, based on which the algorithm then works. This is done so that the user gains an intuitive understanding of ML working principles. Intuitively teaching children the concept of machine learning, much alike how playing with LEGO bricks gives children an intuitive understanding of STEM principles, such statics and center of gravity, among others.
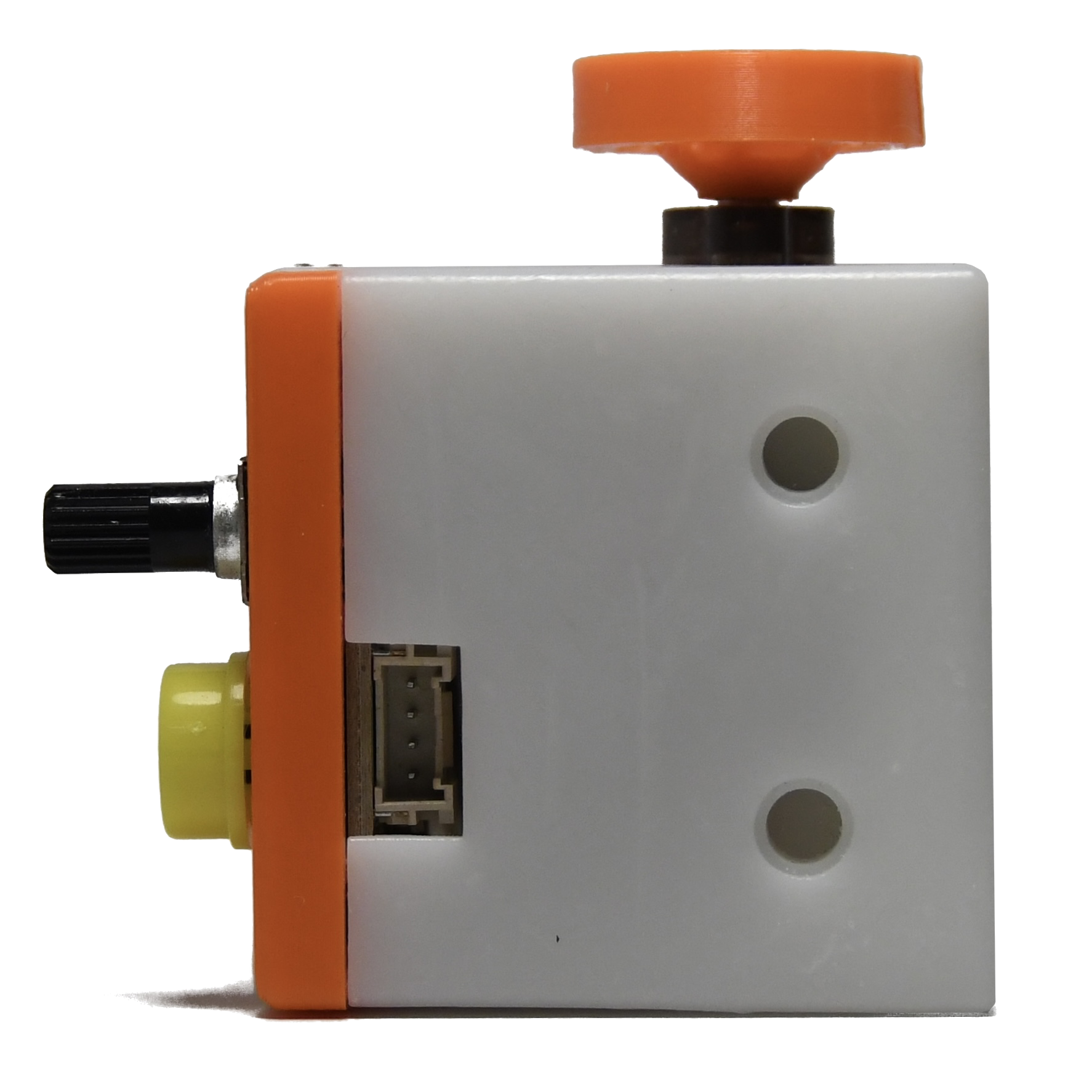
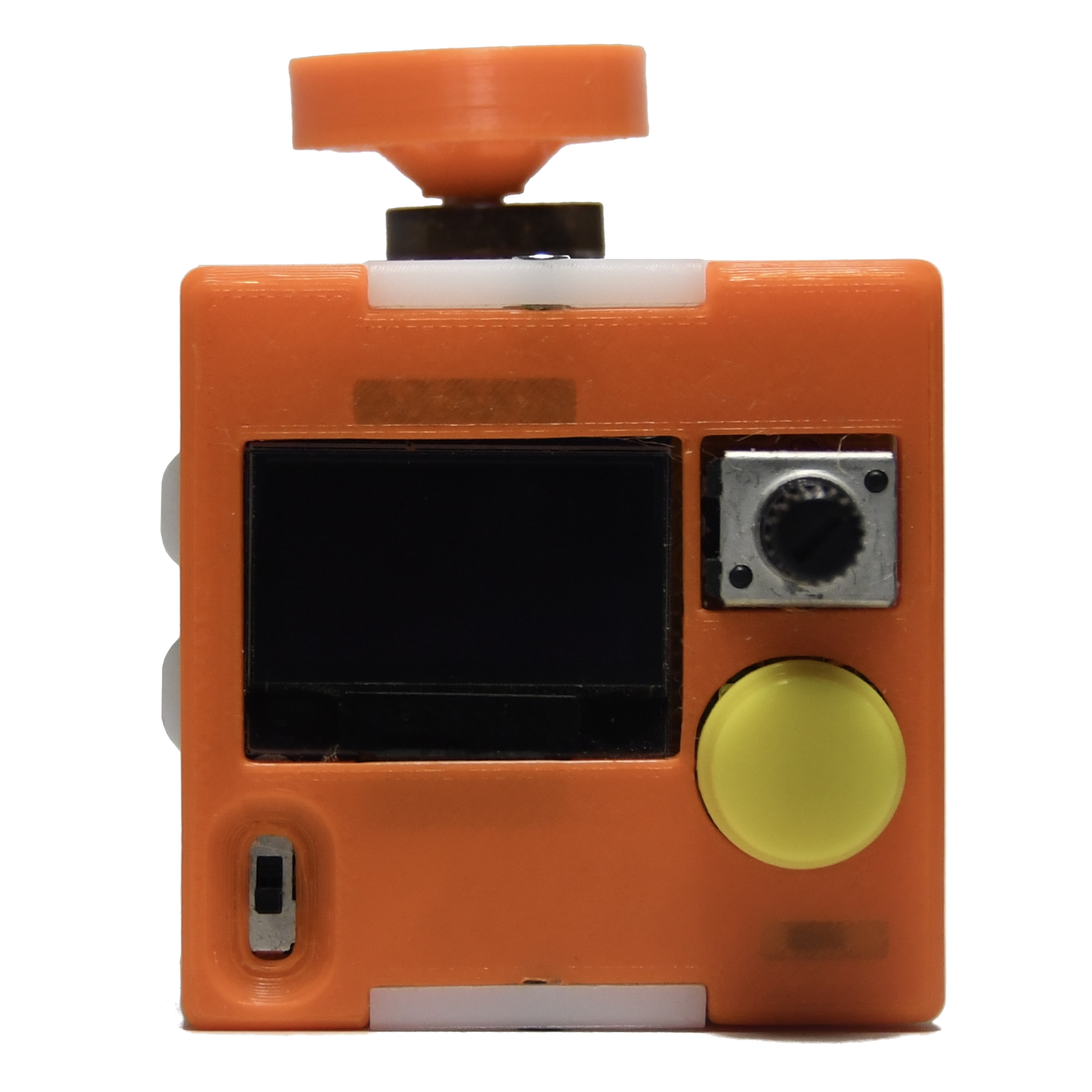


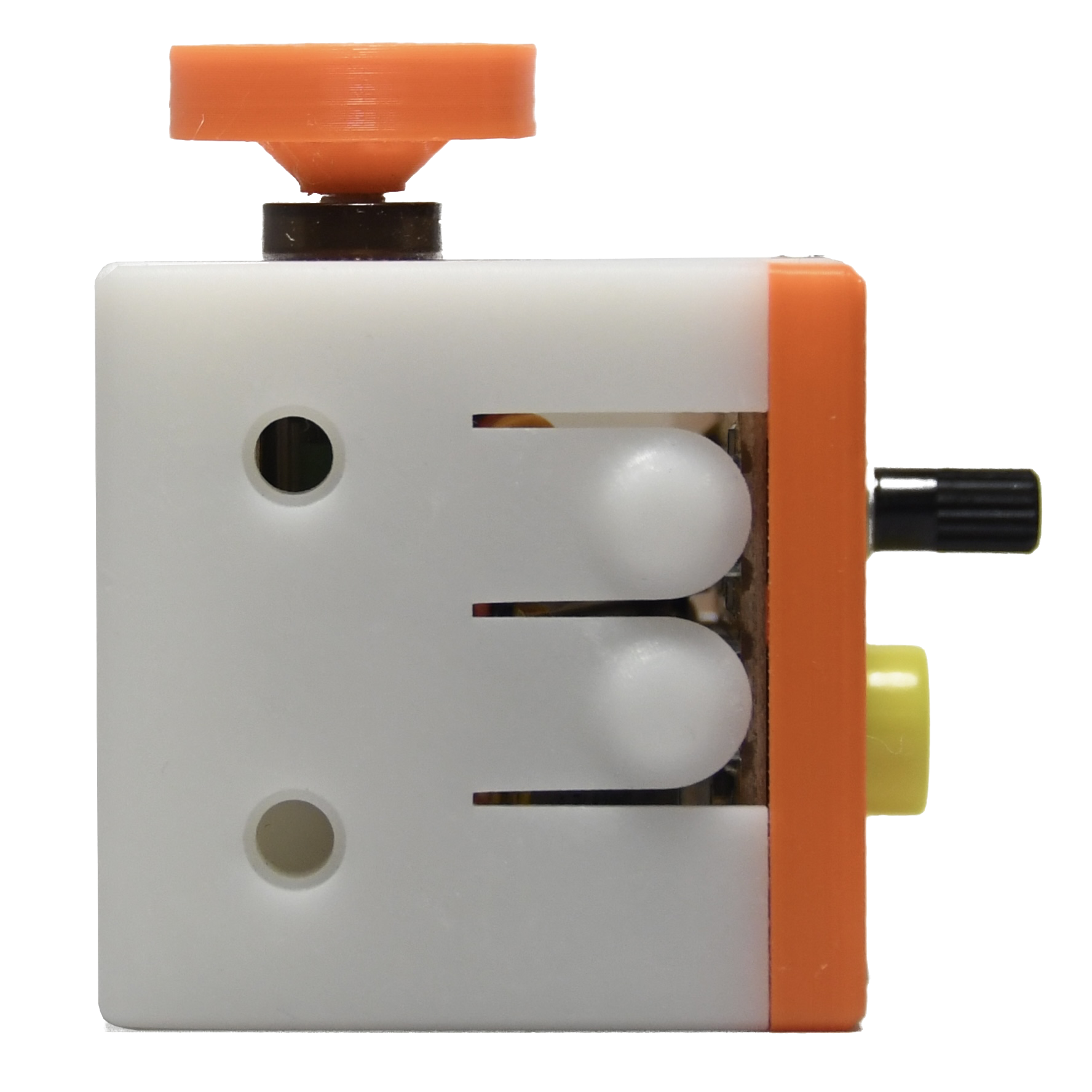 Based on the existing hardware, I designed a peer-to-peer networking approach for Smart Motors. In addition, to facilitate its use and further development, I created an underlying framework architecture called the Smart System Platform.
Based on the existing hardware, I designed a peer-to-peer networking approach for Smart Motors. In addition, to facilitate its use and further development, I created an underlying framework architecture called the Smart System Platform.
 The networking approach consists of a custom networking library based on ESP-NOW, that enables direct communication between any ESP32-based microcontrollers, on which the Smart Modules are based.
The library introduces several features, including an address book system, a message structure with different types and subtypes, and the ability to send larger data packets.
The networking approach consists of a custom networking library based on ESP-NOW, that enables direct communication between any ESP32-based microcontrollers, on which the Smart Modules are based.
The library introduces several features, including an address book system, a message structure with different types and subtypes, and the ability to send larger data packets.
 Building on this, I have created a Smart System Platform add-on library to provide specific commands and handlers to control and configure the Smart Modules.
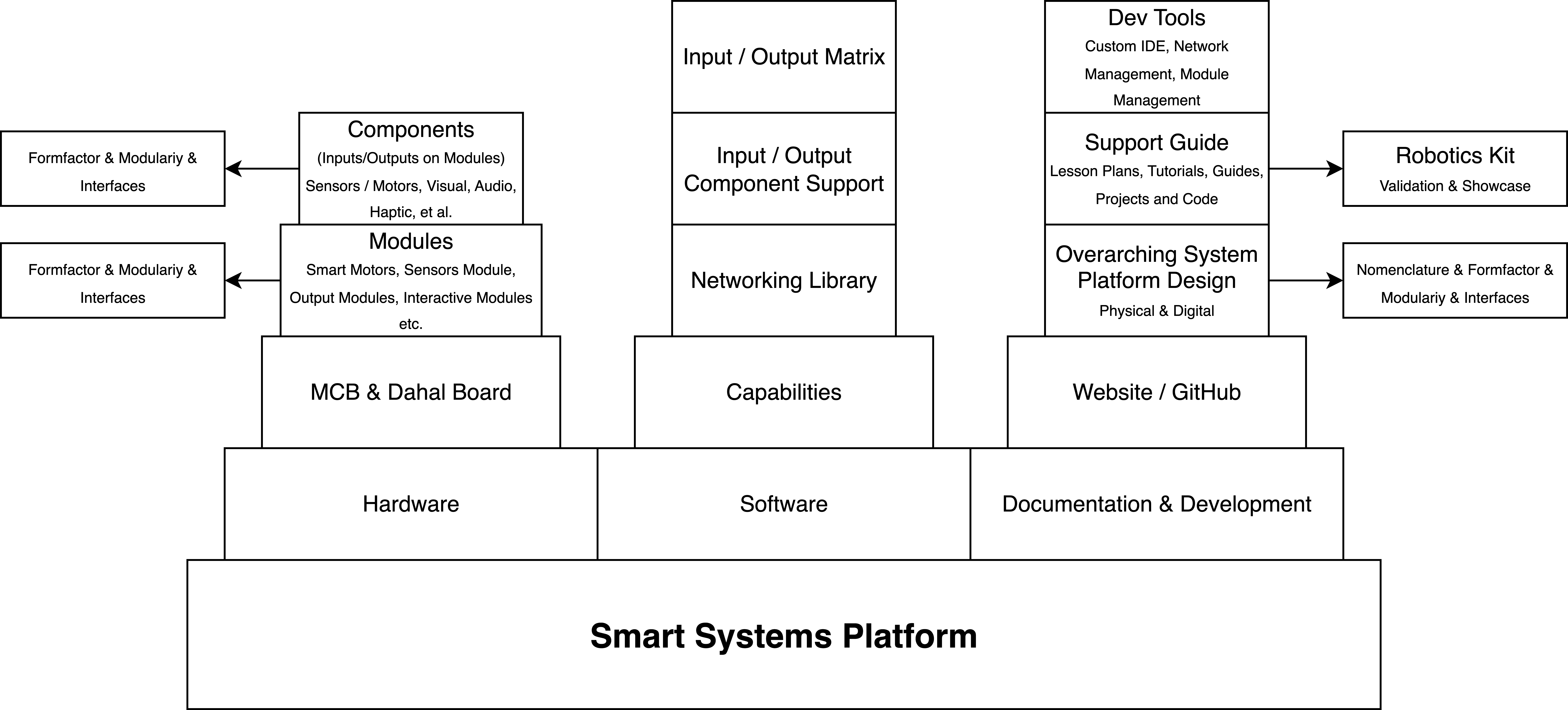
The Smart System Platform has been designed to support and enable access to these networking capabilities, allowing easy interfacing, while serving as an overarching educational robotics system architecture, built around the ESP32 chip, and specifically the Smart Motor Dahal Board.
Building on this, I have created a Smart System Platform add-on library to provide specific commands and handlers to control and configure the Smart Modules.
The Smart System Platform has been designed to support and enable access to these networking capabilities, allowing easy interfacing, while serving as an overarching educational robotics system architecture, built around the ESP32 chip, and specifically the Smart Motor Dahal Board.
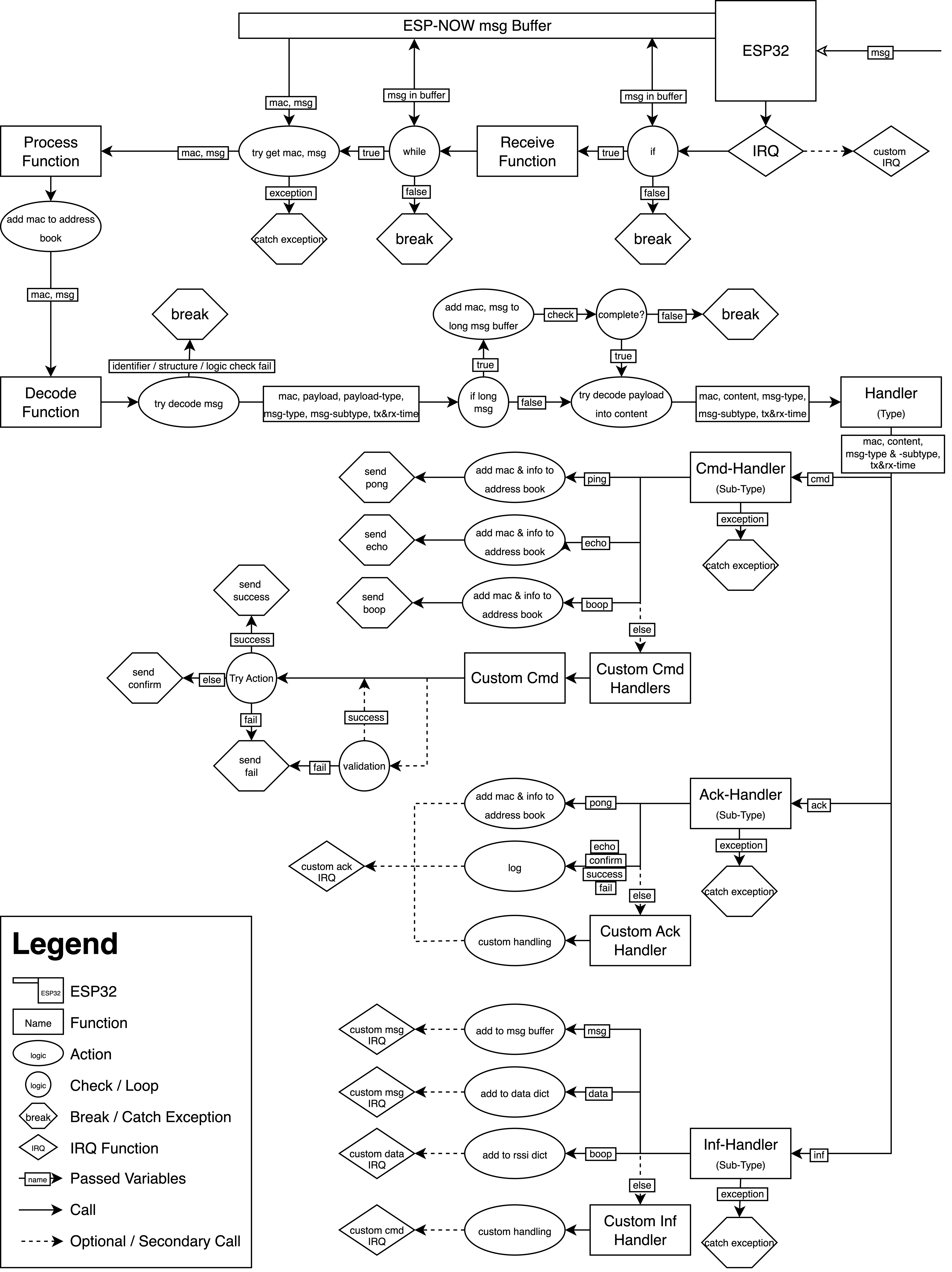
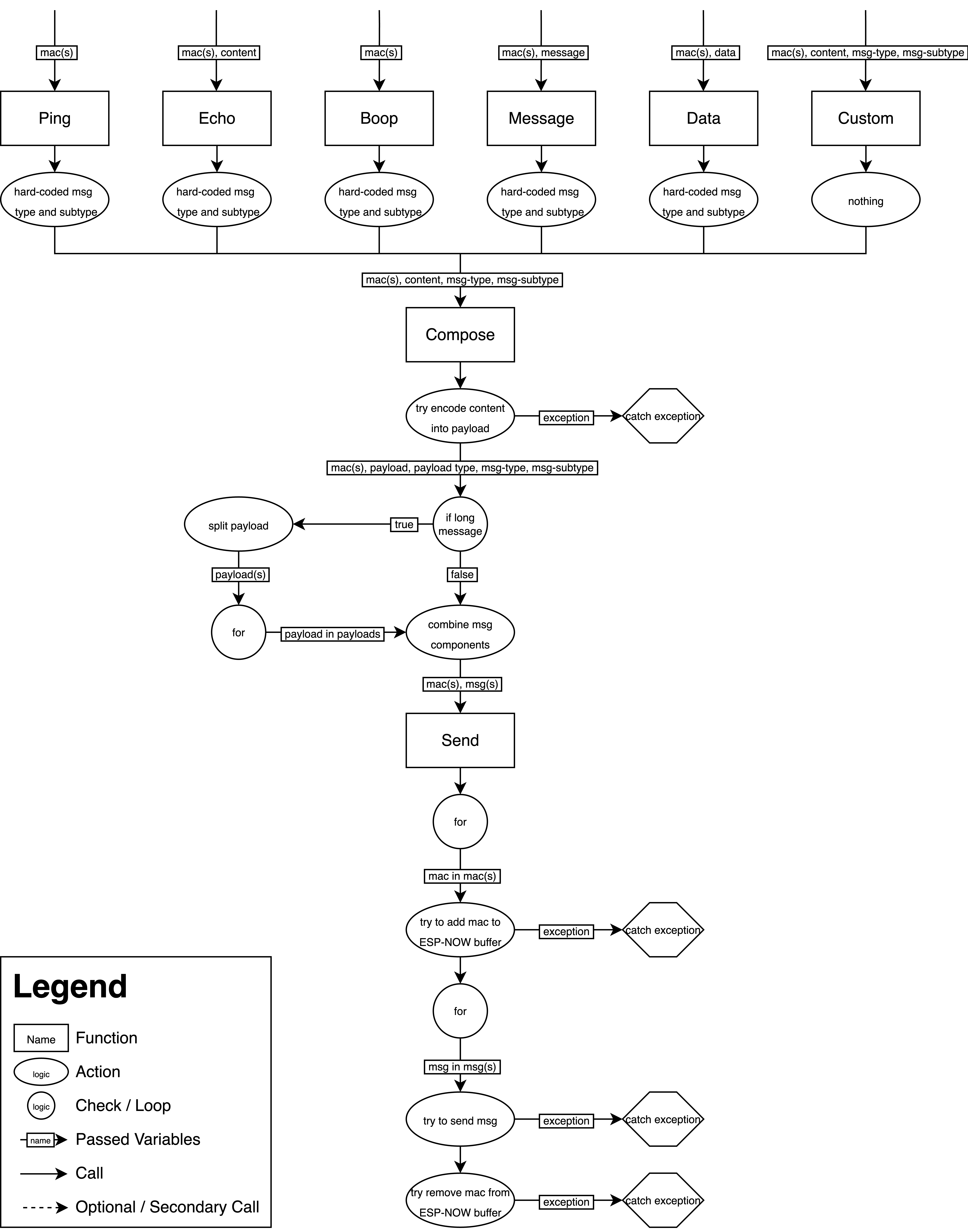 I built a minimum viable product in the form of a number of platform components, including hardware components (with further concepts, as seen in the above figure), software, documentation and development support sites, such as the GitHub page, guides and website, and a suite of networking-focused development and management tools, including a custom web-based integrated development environment.
The developed networking approach and platform were tested using various methods, including robustness tests, experiments with range and received signal strength indicators, and two hackathons with college students to assess their utilisation of the capabilities provided and the application concepts they devised.
The networking approach and platform have also been adopted by students and incorporated into other ongoing research projects, such as the Smart Playground project.
I built a minimum viable product in the form of a number of platform components, including hardware components (with further concepts, as seen in the above figure), software, documentation and development support sites, such as the GitHub page, guides and website, and a suite of networking-focused development and management tools, including a custom web-based integrated development environment.
The developed networking approach and platform were tested using various methods, including robustness tests, experiments with range and received signal strength indicators, and two hackathons with college students to assess their utilisation of the capabilities provided and the application concepts they devised.
The networking approach and platform have also been adopted by students and incorporated into other ongoing research projects, such as the Smart Playground project.
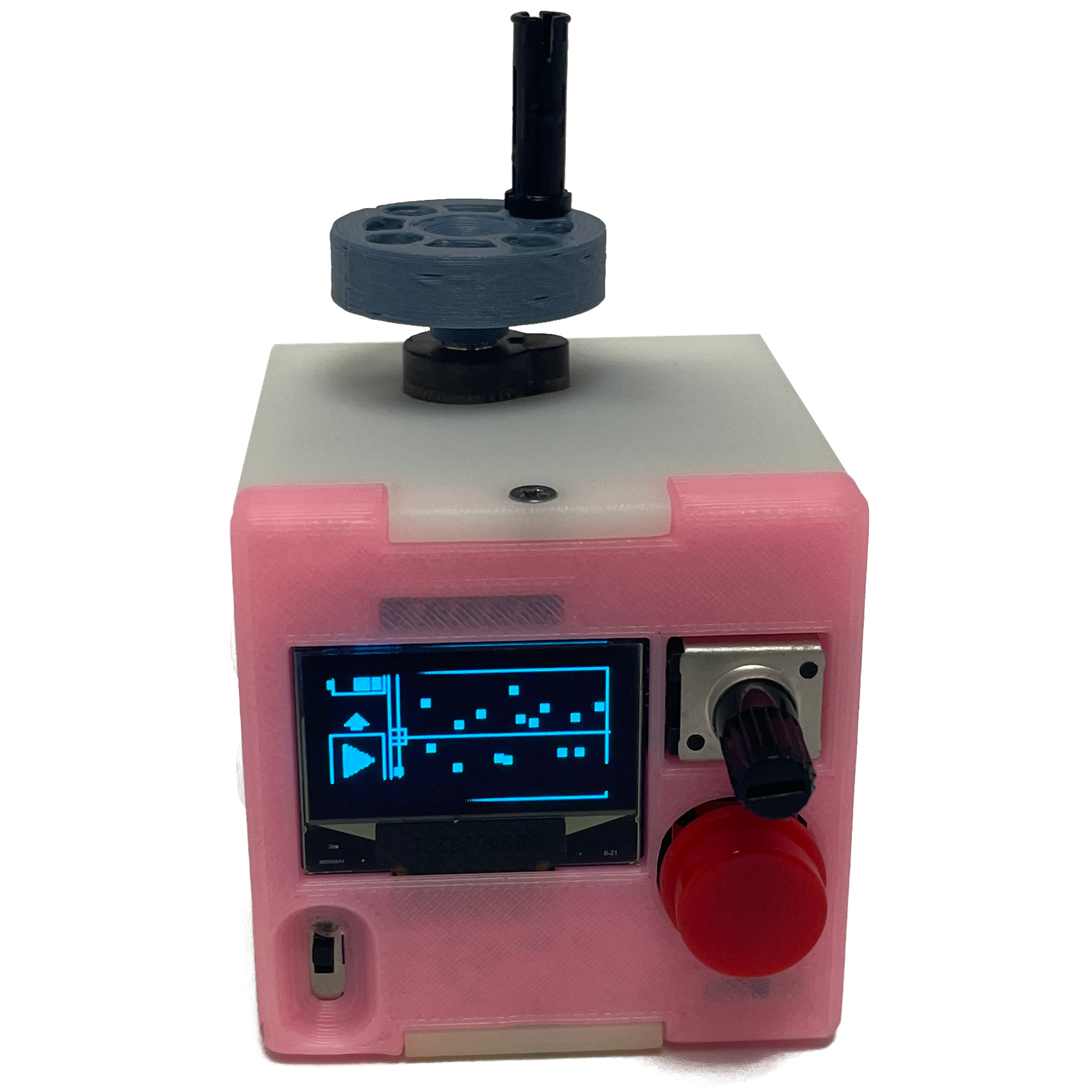


 The outcomes of this research demonstrate the viability of the peer-to-peer communication system and its potential for educational applications. However, the research also highlights shortcomings in the usability and accessibility of the support tools developed.
As with most thesis, a lot of future work could be done on this project, such as improving the quality and accessibility of support tools and materials.
The outcomes of this research demonstrate the viability of the peer-to-peer communication system and its potential for educational applications. However, the research also highlights shortcomings in the usability and accessibility of the support tools developed.
As with most thesis, a lot of future work could be done on this project, such as improving the quality and accessibility of support tools and materials.
This work contributes to the field of educational robotics by providing a flexible, accessible networking solution and support platform that can be built upon to enhance interactive learning environments. The integration of peer-to-peer communication between educational robotics modules and the facilitating Smart System Platform can support and enable novel innovative approaches to STEM education, as well as the development of more complex, collaborative and engaging learning experiences.











This work contributes to the field of educational robotics by providing a flexible, accessible networking solution and support platform that can be built upon to enhance interactive learning environments. The integration of peer-to-peer communication between educational robotics modules and the facilitating Smart System Platform can support and enable novel innovative approaches to STEM education, as well as the development of more complex, collaborative and engaging learning experiences.